The Simulation of Activated Sludge Tanks
What are the benefits of hydrograv simulations?
- Reduced costs by saving energy and investment
- Optimization of biological processes
- Optimization of agitators (location, number, power input)
- Optimization of aeration by determination of the parameters SOTR, SSOTR or SOTE (e.g. according to the German design guidline DWA-M 209)
Example 1: Calibration and validation of the modelling approaches for activated sludge tanks
- Measurement of the 3D water velocities by using a high-resolution acoustic velocimeter
- Calibration and validation of the modelling approaches, e. g. turbulence modelling, bubble size
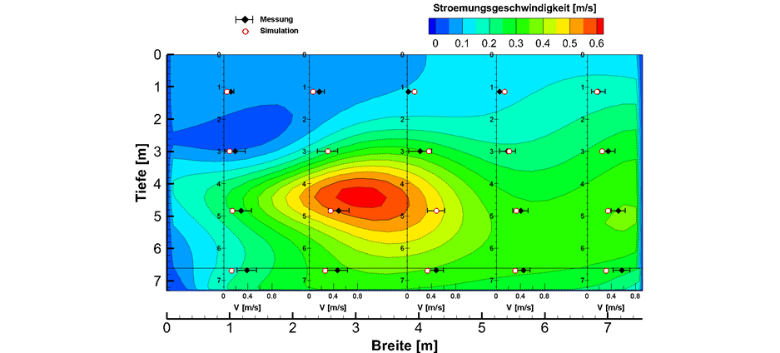
Figure: Comparison of measured and simulated velocities in aerated and anoxic zones in an activated sludge tank.
.
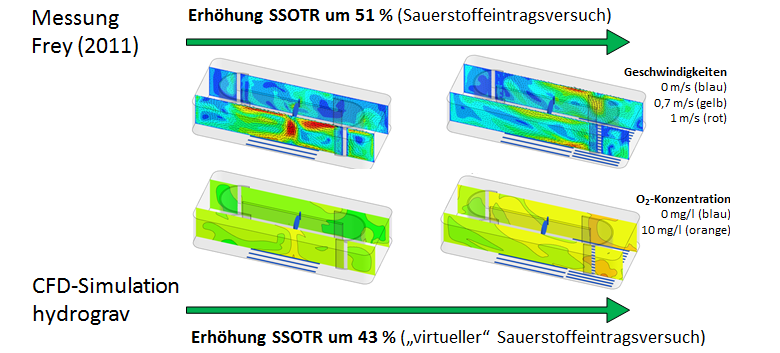
Figure: Comparison of measured and simulated degree of improvment of the parameter SSOTR according the German design guideline DWA-M 209.
Example 2: Optimization of the aeration by simulating the parameter SSOTR-Werten according to the German design guideline DWA-M 209
- virtual oxygen input experiments incl. oxygen transfer by simulation
.
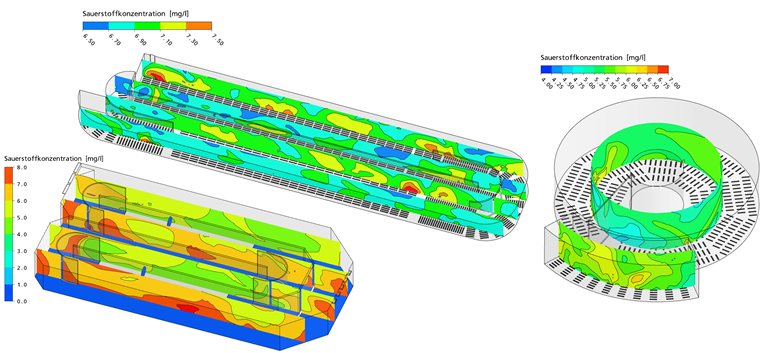
Figure: Concentration of oxygen on planes in different activated sludge tanks.
Example 3: Detection of depositions
- virtual oxygen input experiments incl. oxygen transfer by simulation
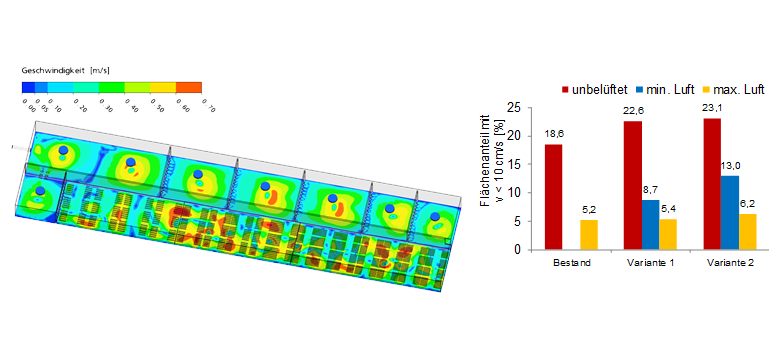
Figure: Velocities close to the bottom in different zones of an aeration tank (left) and deterministic comparison of different variants by analysing areas with velocities lower than a critical velocity (right).
- analysis of concentrations of activated sludge close to the bottom
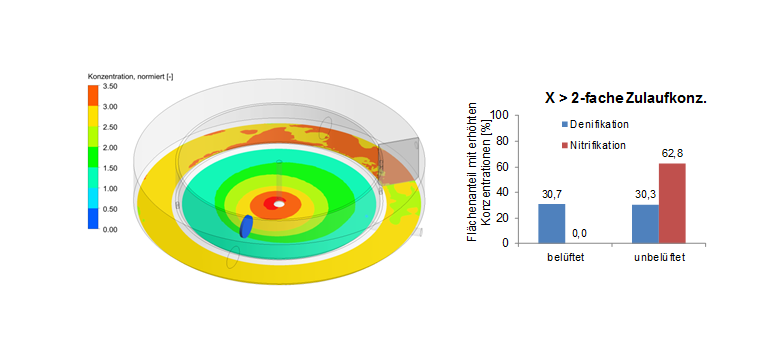
Figure: Concentrations of activated sludge close to the bottom normed with the inflow concentration (left) and determinstic analysis of critical areas with regard to depositions (right).
Example 4: Determination of hydraulic retention time
- simulation und analysis of virtual tracers
- determination of the number of CSTRs (Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors) in series and further statistical parameters
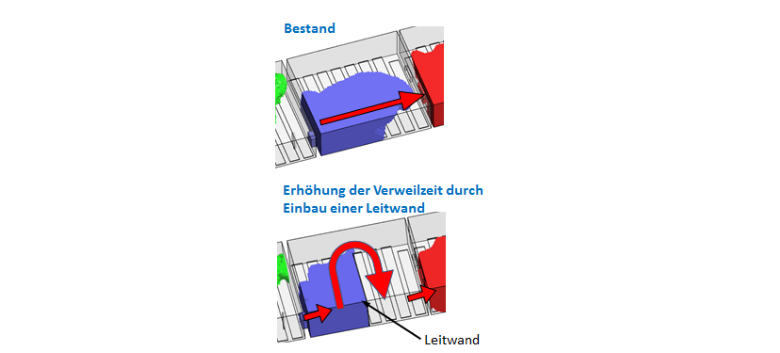
Figure: Exemplare measure for improving the hydraulic retention time to achive a plug flow.
.
