Simulation of Ozone Reactor
What are the benefits of hydrograv simulations?
By increasing the efficiency we minimize construction costs already in the planning stage.
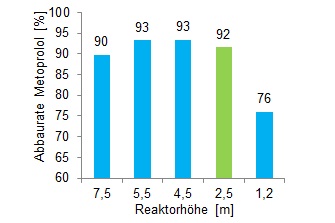
Thus, the volume of the reactor could be reduced by 75 % at the same degradation rate, for example!
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
We maximize the degradation rate of micropollutants, e.g. Metoprolol and Diclofenac by realistic simulation of the reaction kinetics:
- Three-dimensional, multiphase flow simulations
- Modelling of the ozone-oxygen mixture and waste water
- Models to simulate reaction kinetics and for the degradation of micropollutants:
- Ozone transport in the ozone-oxygen mixture and waste water
- Mass transfer of ozone between ozone-oxygen mixture and water
- Decay of ozone
- Reaction with various micropollutants and other substances in water, e.g. DOC
Our goal is maximum forecast reliability by professional measurements!
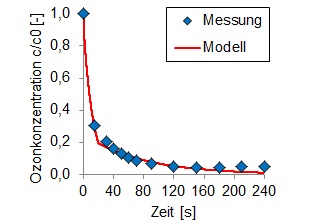
For a realistic simulation of the processes we let perform laboratory measurements for the individual determination of the wastewater-specific reaction rates of the water constituents.
.
.
.
.
.
Validation of the simulation models
Our simulation was developed, calibrated and validated on the basis of a research project „Arbeitsgemeinschaft Spurenstoffe NRW“ (Arge 2011).
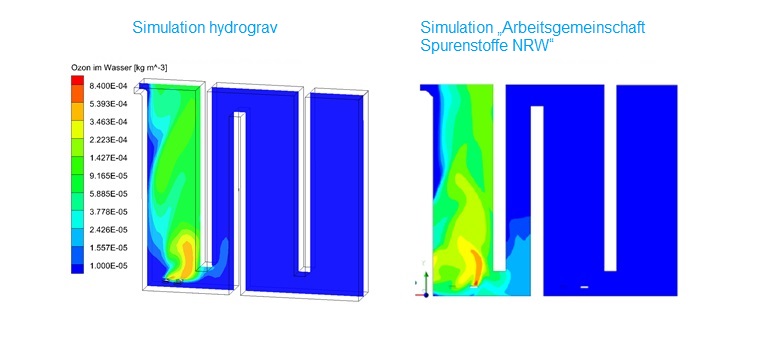
Degradation rates and effluent concentrations
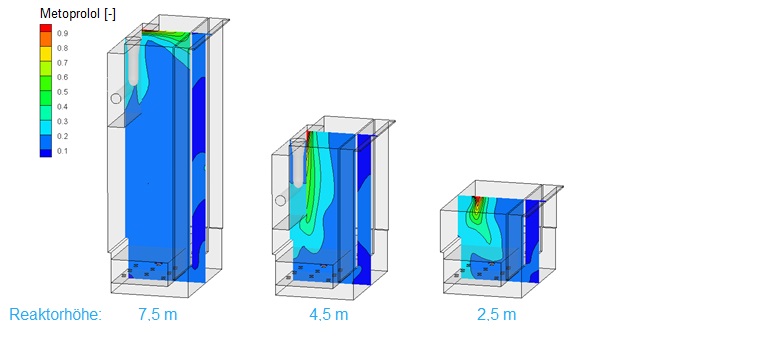
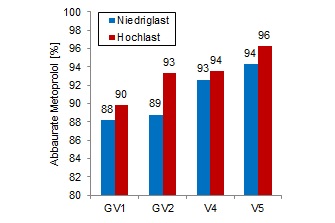 By realistically determining the degradation rates of different micropollutants the overall performance of different variants can be compared. The figure on the left shows the degradation rate of Metoprolol, for example.
By realistically determining the degradation rates of different micropollutants the overall performance of different variants can be compared. The figure on the left shows the degradation rate of Metoprolol, for example.
.
.
.
.
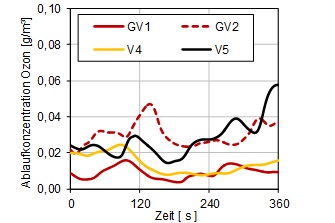
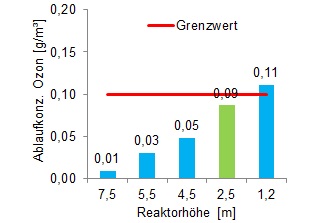
Furthermore, time variable processes can be analysed, e.g. the effluent concentration of ozone – this parameter should not exceed a certain threshold value.
.
.
.
.
.
Better understanding processes by visualization
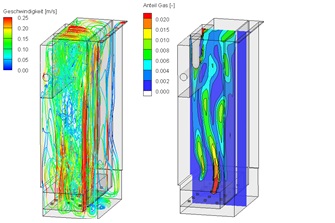 The process understanding of the planning engineer can be improved by various visualizations of the flow patterns and of the distribution of the substances. This provides a further foundation for a more efficient design.
The process understanding of the planning engineer can be improved by various visualizations of the flow patterns and of the distribution of the substances. This provides a further foundation for a more efficient design.
.
.
.
.
Analysis of the residence time distribution
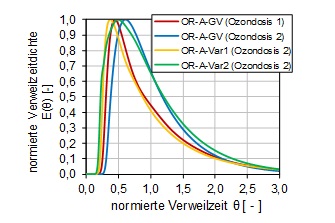
The residence time distribution in the reactor can be realistically determined by using virtual tracers. With statistical analyses short-circuit currents and dead zones can be identified and minimized.
Characteristic values of a tracer analysis are e.g. the numbers of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors (CSTRs) in series or characteristic percentiles of the effluent rate which indicate certain flow patterns.
.
References
